MEASURING PAVER VIBRATOR FREQUENCY
SCOPE
This test procedure describes the method for manual determination of the vibration frequency of each individual internal vibrator on a slipform Portland Cement Concrete (PCC) paver.
PROCEDURE
A. Apparatus
A length of steel rod, 1/2 in. (12.5 mm) in diameter, with a small fork at the lower end to straddle the vibrator body or hydraulic line protector hose. The length of the rod depends upon the distance from about 3 ft. (0.91 m) above the paver operator expanded metal walkway down to the vibrators. The width limit of the fork depends upon the size of openings in the expanded metal walkway. A typical rod might be 1/2 in. (12.5 mm) in diameter by 4 ft. (1.21 m) to 7 ft. (2.13 m)-long with a 2 in. (50 mm) fork opening (Figure 1).
Tachometers: (Figure 3)
· Vibra-Tak®, single wire reed type.
· Standco®, vibrating reed type.
Note: A Vibra-Tak®, single wire reed type tachometer, is sometimes preferred as it has a wide range of frequency, is low-cost, durable and gives readings with acceptable accuracy.
B. Recording Procedure
Take vibrator readings immediately after the start of paving and the following:
· When electronic vibration monitoring is used, check and record frequency on a minimum of two random vibrators daily.
· When electronic vibration monitoring is not used, check and record frequency of each vibrator twice daily.
Take readings after any changes are made to the vibrator.
C. Taking Readings
In most cases, the best readings can be obtained through contact with the hydraulic line protector hose just above the vibrator (position A, Figure 2). The second choice location would be position B (Figure 2). Taking readings directly from the vibrator body (position C, Figure 2) may be excessively harsh, hard to read, and could eventually damage the tachometer-testing apparatus.
Vibration transmission to the tachometer is obtained by placing the lower end of the forked rod on or near each vibrator (Figure 2) while reading the vibrations per minute (VPM) value from the tachometer at the top of the rod. (Caution, do not allow the metal rod to touch any other part of the paver, such as the metal walkway, while taking readings.)
Vibration readings are obtained by holding the nose of a wire type Vibra-Tak® against the top end of the rod, perpendicular to the rod axis. As the wire reed of the Vibra-Tak® is moved in or out of its holder, by moving the tuning slide, a maximum reed vibration will occur at a specific reed length. Read the VPM (x 1000) on the reed holder body adjacent to the top rim of the tuning slide. Standco® readings are taken directly from the tachometer (Note: Be aware that resonant harmonics from lower frequencies (1800 vpm) can invoke a response at a higher frequency (3600 vpm) with lower amplitude.
D. Specifications (Refer to Article 2301.03.)
E. Report – Report results on Construction Manual Appendix 9-3 “Project Information/Paver Inspection” (Form 830213).
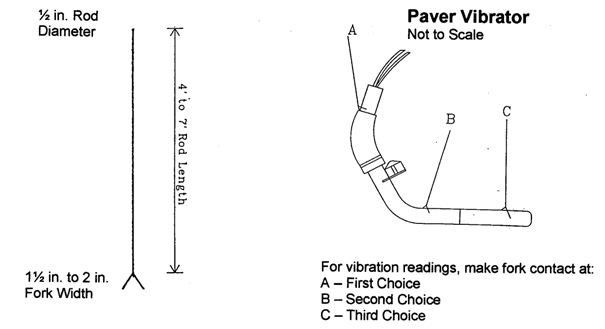
Figure 1 Figure 2
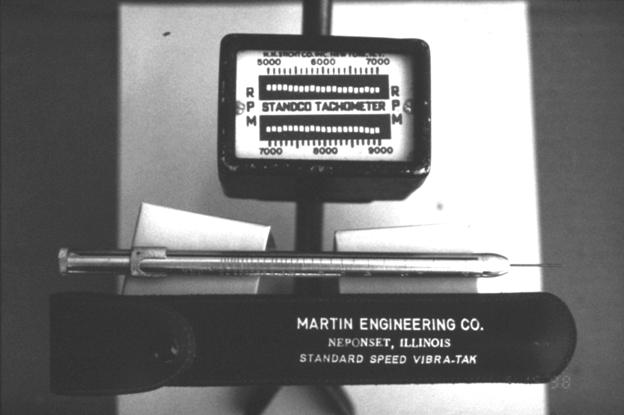
Figure 3 – Vibrating reed type and single wire reed type tachometers.