GENERAL
Acceptance of materials relating to structural steel fabrication is based on producer or supplier certifications, or by acceptable test results of samples obtained by a representative of the Iowa DOT. Sample arrangements and locations will be determined after copies of fabricator purchase orders for all materials required (except structural steel) have been received by the Iowa DOT Construction and Materials Bureau.
All products of iron, steel and/or coatings shall be of domestic origin, melted and manufactured in the USA and shall also comply with the Buy America requirements in IM 107. The fabricator shall certify by letter to the Iowa DOT that these materials are of domestic origin.
Listed below are the inspection requirements and the basis of acceptance of various materials used in structural steel fabrication. For acceptance procedures of items not listed below, contact the Iowa DOT Construction and Materials Bureau (Structural Materials Engineer).
A. Structural Steel
1. Grades of Steel
ASTM A709
|
Grade US |
Yield Strength, ksi |
Grade Non-fracture Critical-Charpy |
Grade Fracture Critical Charpy |
|
36 |
36 |
36T |
36F |
|
50 |
50 |
50T |
50F |
|
50S |
50 |
50ST |
50SF |
|
50W |
50 |
50WT |
50WF |
|
HPS 50W |
50 |
HPS 50 WT |
HPS 50 WF |
|
HPS 70W |
70 |
HPS 70 WT |
HPS 70 WF |
|
100 |
100 |
100T |
100F |
|
100W |
100 |
100WT |
100 WF |
|
HPS 100W |
100 |
HPS 100 WT |
HPS 100 WF |
W signifies weathering.
Other steels may be used as required by the contract documents or as approved by the engineer.
2. NOTE 1: Grade HPS 70W, 100, 100W, or HPS 100W shall not be substituted for Grade 36, 50, 50S, 50W, or HPS 50W.
NOTE 2: Grade 50W or HPS 50W shall not be substituted for Grades 36, 50 or 50S without prior approval of the Structural Materials Engineer.
NOTE 3: Non-fracture critical, T, components and fracture-critical, F, components shall be impact tested in accordance with ASTM A673 requirements and shall meet the requirements listed in Table 9 and Table 10 of ASTM A709 respectively.
3. Basis of Acceptance of Structural Steel
Structural steel will be accepted on the basis of Mill Test Certifications and physical inspection at the fabrication site. Mill Test Reports need not be notarized, but must bear the name and signature of a responsible representative of the company. Mill Test Certifications shall clearly show the origin of the material.
The shop inspector shall be given Mill Test Certifications in triplicate at the earliest possible date prior to the fit-up stage of bridge fabrication. Upon receipt of the Mill Test Certifications, the quality control inspector will check the physical and chemical test results to determine compliance with the designated grade of steel and the Build America, Buy America requirements. Charpy test results shall be actual figures of individual test. When compliance has been determined, the inspector will date and initial the certifications.
Certification of compliance from a steel supplier in lieu of a Mill Test Certification is acceptable providing actual test values are shown and a responsible representative of the supplier signs the certification.
4. Physical Inspection of Structural Steel by the Quality Control Inspector at the Fabrication Plant
a. Dimensions
Thickness of flange plates, cover plates, web plates and webs and flanges of rolled beams shall be measured to the nearest .001 inch.
Width of flange plates, cover plates and the flanges of rolled beams shall be measured to the nearest 1/16 inch.
Depth of rolled beams and welded girders shall be measured to the nearest 1/16 inch.
Thickness and width of structural steel used as main members except those listed above shall be measured to the nearest 1/16-inch.
b. Determining Mass Compliance of Rolled Beams
Shop inspection to determine the mass of rolled beams shall be by the following method:
1) Measure the flange thickness and record the average flange thickness
2) Measure the web thickness and record the measurement
3) Add the theoretical thickness of one flange and the web
4) Add the actual (average) measured thickness of the web and the actual (average) thickness of the flange measurements.
5) Subtract the "actual measured" total from the theoretical total.
6) Divide this difference by the theoretical total and multiply by 100 to secure percent underweight (the specified mass tolerance is minus 2.5 percent).
The Structural Materials Engineer shall be contacted when the formula indicates a beam is outside of tolerance. Location of the beam in the structure will be a factor in determining status of beam, which is outside of allowable tolerance. Actual weighing of beam may be required.
c. Mill Rolling or Handling Defects
Laminations - edges, longitudinal, and transverse. (See AWS D1.5 Specifications for limitations and method of repair.) Contact the Structural Materials Engineer for the final disposition of laminations.
Other defects - (rolled in foreign material) surface scabs, fins. Determine the approximate width and depth of defective area. Contact the Structural Materials Engineer for instructions for possible repair.
Other defects – waviness, sweep, kings, & gags. Determine the extent of the defective area. When outside allowable tolerance, corrective action will be required in accordance with IM 563, Section IV. Straightening of Materials.
d. Flame Cutting Defects (See IM 563.)
e. Heat Correcting of Steel. (See IM 563.)
B. Swedge Bolts & Tie Rods (See IM 453.08)
1. Bolt Acceptance
Steel for tie rods shall be ASTM A-36 or other approved grade. Steel for swedge bolts shall be ASTM F1554 Grade 36. Steel for swedge bolts and tie rods shall be accepted by Mill Test Report, Iowa DOT testing and from an approved supplier.
2. Nuts & washers
Nuts shall meet the requirements of ASTM A-563 DH (Heavy Hex). Washers shall meet the requirements of ASTM F-436.
3. Shop Inspection of Swedge Bolts & Tie Rods
a. Dimensions
1) Diameter
2) Length
3) Thread length
4) Deformations (swedge bolts)
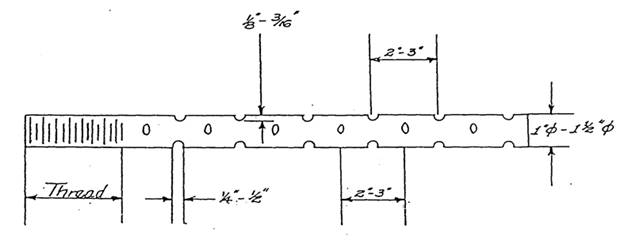
Typical Swedge Anchor Bolt
Swedge anchor bolt requirements
1. Indentations shall be formed by displacement of metal in a staggered pattern. No cutting shall be allowed to form the indentations
2. Four rows of indentations
3. Indentations can either be oblong or round in shape
4. Depth of indentations: 1/8” – 3/16”
5. Indentation shall form a minimum ¼” radius in the bottom of the groove, “V” shaped grooves are not allowed
6. Width of indentations: 1/4” – 1/2”
7. Spacing between indentations: 2.0”-3.0”
8. Anchor bolts shall be set in accordance with article 2405.03H2 of the Standard Specifications
C. Shear Studs (AWS D1.5 Stud Welding)(IM 453.10)
1. Acceptance
Acceptance of shear studs is based on Mill Test Certification showing actual results of tests conducted not more than six months prior to the date of delivery of the studs. Approved sources are listed in IM 453.10, Appendix A.
D. Castings
1. Steel & Iron (Standard Specifications, Sections 4153.03 & 4153.04)(IM 453.04)
A sample of each heat shall be submitted to the Iowa DOT for testing. The identification form accompanying the sample shall have the following:
a. Pour date
b. Heat number
c. Casting type grade
d. Number of pieces
Each casting shall be marked with heat number for identification. Castings shall be visually inspected for pouring deficiencies or damage in accordance with IM 563, Section VI. Machining Inspection.
2. Bronze Castings (Standard Specifications, Section 4190.03)
Approval of bronze bearing plates is based on the correlation of test bars submitted to the Iowa DOT by the supplier and the test results of the manufactured plates sampled at the fabricator's plant by the Iowa DOT inspector. One plate shall be submitted for testing representing each heat from which castings were poured. A manufacturer's certification showing actual test results in also required.
Inspection of dimensions, inserts and finish shall be conducted on the samples submitted to the Iowa DOT.
Approved fabricators are listed in IM 557, Appendix B.
E. Pins & Rollers (Standard Specifications, Section 4153.02)
1. Cold Drawn Steel
Cold drawn steel for pins and rollers is accepted by Mill Test Certification providing that in addition to the chemical analysis, either the hardness or tensile strength is recorded. If this information is not shown on the certification, a test sample is required.
2. Forged pins or rollers (Standard Specifications, Section 4153.01)
F. Bolts, Nuts & Washers (Standard Specifications, Section 4153.06)
Approval of bolts, nuts and washers is based on test results of samples selected and submitted to the Iowa DOT Laboratory by a representative of the DOT. High strength bolts, nuts and washers shall be marked as prescribed in ASTM A-325. The sampling frequency shall be as listed in IM 453.06B.
G. Paint (Standard Specifications, Articles 2508, 4182)
All painting of structural steel shall be performed in the shop and shall be inspected in accordance with IM 567.
H. Electrodes & Flux (IM 559)
Acceptance is based on a list of approved brands for which satisfactory test reports have been made within the last year by the manufacturer. Random filler metal tests may be required to substantiate manufacturer test results.
I. Galvanized Material (Standard Specifications, Section 4100.07)
An electromagnetic thickness gauge either at the fabricating plant or at the job site shall inspect galvanizing thickness. Galvanized hardware shall be sampled and submitted to the Iowa DOT Central Laboratory for testing.
J. Aluminum Handrail & Hardware (Standard Specifications, Section 2414.05 E)
Acceptance is based on certification checked and approved by the Iowa DOT Laboratory, Ames, Iowa. Approved fabricators are listed in IM 557, Appendix B.
K. Anchor Bolts (See IM 453.08)
All high strength anchor bolts, shall be accepted on the basis of sampling and testing and Mill Test Report and from an approved supplier.