80 feet)
centers to effectively close passing lane
Remove impact attenuator and all temporary barrier rail at upstream end
Remove any advance construction work zone signing in the direction towards
oncoming traffic
The entire removal operation shall proceed upstream towards traffic. This will
ensure that motorists will have two clear open lanes once they pass traffic control
removal operations. Tubular markers shall not be removed in any area until the double
yellow lines are removed, unless they are replaced with 42 inch channelizers.
Tubular Markers
Specification Article 2528.03
requires tubular markers be covered with reflectorized sheeting. The specified height
range is between 700 to 850 mm (28 to 34 inches), so most traffic control subcontractors
reuse tubular markers hit by vehicles by cutting off the bottom 150 mm (6 inches). Since
the bottom 150 mm (6 inches) of the tubular marker will eventually be cut off, this area
does not need to be covered with reflectorized sheeting.
Many tubular markers used on projects are manufactured extruded plastic shapes.
These shapes typically are not exactly round in order to provide for greater strength
for the tubular marker. When non-round tubular markers are used on projects, care needs
to be taken in their initial installation so that the tubular markers are placed on the
centerline of the highway with the non-round side placed facing alternating directions
from one tubular marker to the next. This placement orientation will optimize the overall
retroreflectivity of the TLTWO (two-lane, two-way) delineation system.
Raised Pavement Markers
Many interstate or other complex project traffic control plans include the use of
raised pavement markers to supplement the temporary pavement markings for the project.
Raised pavement markers are used in lane shifts or at crossover locations to enhance
visibility of correct travel path through these areas. Raised pavement markers are
very effective if they stay in correct location on pavement surface.
Off-tracking rear wheels on semi-trailers often dislodge raised pavement markers from
the pavement surface. It is permissible to offset the location of the raised pavement
markers up to 225 mm (9 inches) laterally away from the temporary pavement marking line
to avoid the off-tracking rear trailer wheels. See Standard Road Plan
TC-61 for typical applications for
median crossovers.
5.31 CHANGEABLE MESSAGE SIGN GUIDELINES
More projects are using Iowa DOT or contractor furnished changeable message
signs. These CMS units are intended to be used for incident management traffic
control, advance lane closure information or other additional motorist information
that needs to be timely, emergency response, temporary road closures for bridge
beam replacement, temporary utility crossing requiring road closure, and for other
emergency related road closings.
If CMS units are used according to detail sheets contained in project plans,
the word message shall be according to the plan sheet requirements. CMS
units used for incident management traffic control for major interstate
reconstruction projects should have the word message approved by the State
Traffic Engineer, since the appropriate message will vary from project to
project. CMS units used for all other situations should also have the word
messages approved by the State Traffic Engineer. Proposed word messages should
be limited to a maximum of 2 panels and usually 8 words or less per panel.
Additional information relating to the use and operational guidelines for the
Department's CMS units is included in the Guidelines for Changeable Message
Signs. This guideline is available form the State Traffic Engineer, Office of
Traffic and Safety at (515)239-1513.
If CMS units are used according to detail sheets contained in project plans, the
word message shall be according to the plan sheet requirements. CMS units used
for incident management traffic control for major interstate reconstruction projects
should have the word message approved by the State Traffic Engineer, since the appropriate
message will vary from project to project. CMS units used for all other situations should
also have the word messages approved by the State Traffic Engineer. Proposed word messages
should be limited to a maximum of 3 panels and usually 8 words or less per panel.
Distribution of Department owned CMS units used for project
purposes will be under control of the district traffic technicians. The traffic technicians
will coordinate the logistics and placement of the portable CMS units used on construction
projects statewide. Repair costs for Department owned CMS units
used for project related incident management can be charged against project funds using the
appropriate documentation.
Additional information relating to the use and operational guidelines for CMS units is included in the Guidelines for Changeable Message Signs.
This guideline is under the auspices of the Office of Traffic and Safety. Comments
regarding the Guidelines should be directed to the State Traffic Engineer at 515/239-1513.
5.32 ARROW DISPLAYS
Solar Assisted Arrow Displays
Solar assisted arrow displays have been effectively used in Iowa since 1991. A listing
of approved solar assisted arrow displays is found in Materials
I.M. 486.12.
Manufacturers of solar assisted arrow displays not currently approved for project use may
contact the State Traffic Engineer at 515/239-1513 to schedule a field review in order to
be on the approved list.
If any solar assisted arrow display fails to perform adequately in a field situation, it
shall immediately be removed and replaced with a different arrow display. The Office of
Construction should be informed if any approved solar assisted arrow display fails to
perform so that the deficient arrow display model can be deleted from the approved list.
Vehicle Mounted Light Bars
Some traffic control manufacturers are producing small, vehicle mounted light bars to
be used as an arrow display. Typical units are the ArrowstikTM or Traffic
GuideTM. These types of arrow displays do not meet the minimum requirements
of the specifications which require the use of Type C arrow displays. A Type C arrow
display is required to be 2.4 m x 1.2 m (96 inches x 48 inches) in size. Therefore, these
smaller light bars are not acceptable for use on our projects as arrow displays. They may
be used in a wigwag or non-directional mode as an additional warning device.
5.33 TEMPORARY CONCRETE BARRIER RAIL
Temporary barrier rail is used on projects to protect the work area from
traffic intrusion. Traffic that contacts the barrier is deflected along the
barrier without being bounced back into open traffic with minimal barrier
offset. Iowa uses an F-shape temporary concrete barrier rail system that is
NCHRP 350 approved. This barrier uses a pin/loop connection between sections and
is capable of being tied down to the underlying pavement.
Temporary concrete barrier rail is typically used in the following applications:
- To separate two-way high volume traffic
- To prevent motorist intrusion into a potentially hazardous work area
- To provide positive protection for workers in the work area
- To protect the highway facility itself, such as temporary structural shoring
Temporary barrier rail is a hazard in itself. Temporary barrier rail should not normally
be used where it is a greater hazard than what it is protecting. At least 0.6 m (2 feet)
clearance should be provided behind the rail for drop-offs less than 600 mm (24 inches). At
least 1.2 m (4 feet) clearance should be provided behind the rail for drop-offs greater than
600 mm (24 inches). When these conditions cannot be met, the temporary barrier rail should be
tied down to the underlying pavement according to details provided in
Standard Road Plan RE-71.
If location is such that Standard Road Plan RE-71
cannot be used to properly anchor the temporary barrier rail, contact the Office of Construction for
additional details. On projects where field conditions result in a drop-off as described above but do
not include Standard Road Plan RE-71, the tie-down
devices necessary will be extra work.
5.34 SIGN MOUNTING TYPES
Specification Article 2528.02
states that signs for traffic control zones in duration for 4 calendar days or longer are
required to be post mounted. Signs for traffic control zones in duration shorter than 4
calendar days may either be post mounted or skid mounted. The intent of this specification
is to require post mounting of signs where the project is not a moving or temporary situation.
The 4 calendar days should be based on the planned construction operation for the specific
traffic control zone setup. Weather delays shall not require that skid mounted signs be changed
to post mounted signs to meet the intent of this specification. All post mounted signs are required
to be mounted 2.15 m (7 feet) above the surface of the pavement according to the specifications.
In urban areas, signs that require post mounting may be skid mounted at the post
mounting heights required in the MUTCD provided that skid mounting devices are NCHRP
350 compliant, so they would not become a hazard if hit by vehicles.
U Channel
Posts
Specification 2528.02 allows 3 pound
per foot U Channel posts as one of the three post mounting options for work zone signs.
An easy way to determine if the supplied post is a 3 pound per foot post, use the image
at right and dimensions as a guide. |
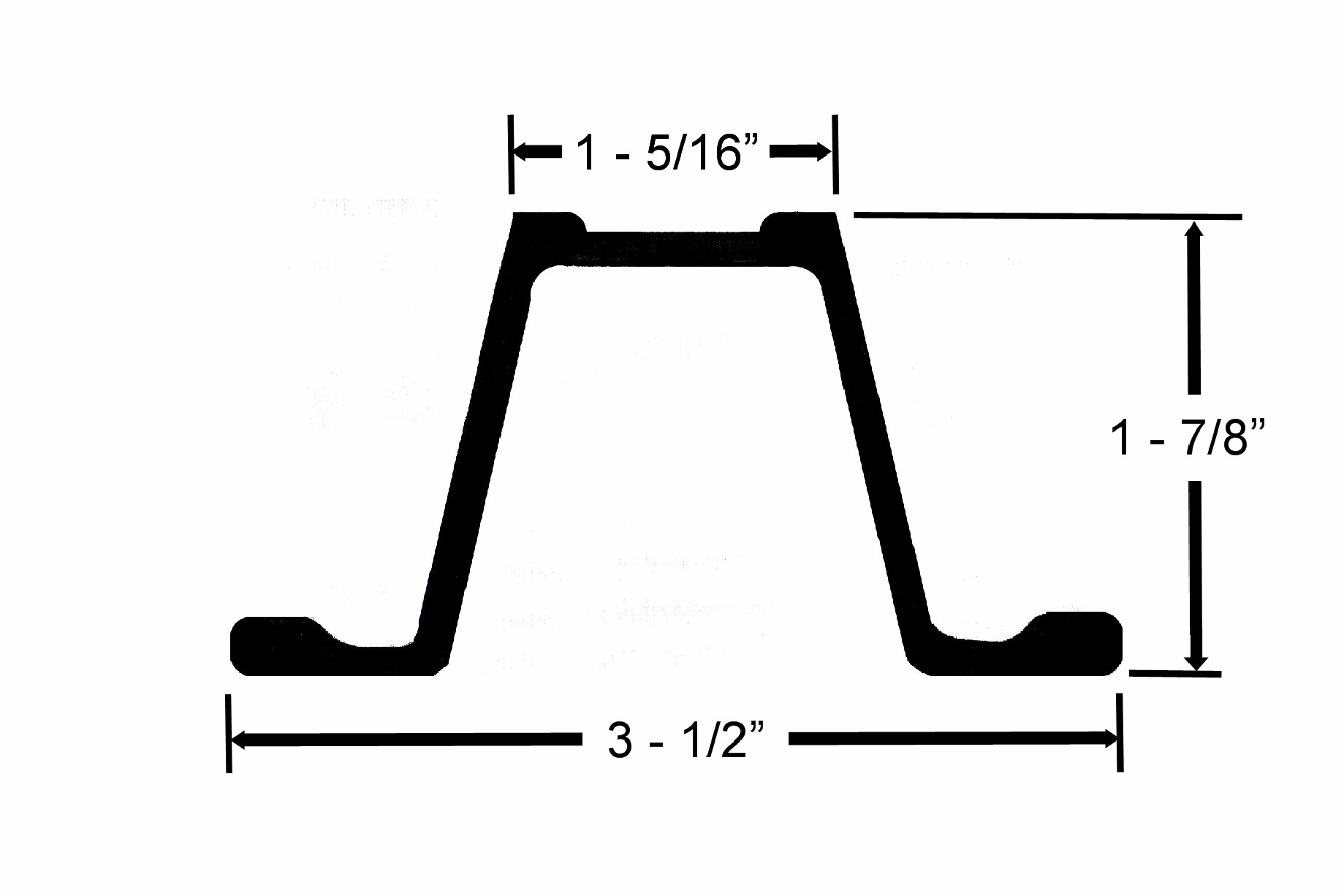 |
5.35 REMOVAL OF TEMPORARY PAVEMENT MARKINGS
Temporary pavement markings are necessary for most construction projects. Typical
locations include runarounds, diversions, stage construction, etc. When temporary
pavement markings are placed, they will eventually be removed as part of the project.
Removal depends on the type of pavement marking material placed and type of surface
to which it is attached (new or old, HMA or PCC). Two types of temporary pavement
markings are currently used: removable pavement marking tape and heavy metal free
waterborne paint.
Pavement Marking Removal Characteristics
Each temporary pavement marking material has its own removal characteristics:
- Removable Pavement Marking Tape
This material has an average thickness of 8 x 10-3 to 2 x 10-2
mm (30 to 70 mils). It is precoated with pressure sensitive adhesive, adheres well under
traffic, and also removes without a trace. This is the only material now available for use
on diagonal lines per Specification 2527.06.
This material is the most expensive of the two temporary pavement marking materials.
- Temporary Painted Pavement Markings
This material is the most commonly used
material for temporary pavement marking due to its economical price. It requires removal according
to Specification Article 2527.03.B. Temporary
painted pavement marking materials must satisfy requirements of
Specification Sections 4183 and 4184.
- Removable, Non-reflective, Preformed Tape
In lieu of removing the existing permanent pavement markings, contractors may
elect to cover them with removable, non-reflective, preformed tape. This material
is designed to be applied over the existing markings and then can easily be removed
from the pavement’s surface without damaging the underlying pavement markings. It
is rather expensive, but it does have the advantage of not requiring removal,
installation, and re-removal of a pavement marking to delineate the construction
work zone.
Disposal of Removed Pavement
Marking Materials
All pavement marking removal operations shall be completed in
accordance with Specification Article 2527.03.B.
This article requires that removal operations be essentially dust free and collect all of the
removed product from the road surface. Typical pavement marking removal operations consist of
dry vacuum grinding, shot blasting, or water blasting. All removed pavement marking materials
shall be disposed according to the following Iowa DNR requirements:
- Pavement marking waste (including water) may remain on the roadside (granular
or earth shoulders and foreslopes) with the following exceptions, as long as it is
removed from the pavement surface itself. The waste may not be discharged directly
into a stream or storm sewer or where it would likely runoff into a waterway. Linear
disposal of pavement marking waste along the roadside should not cause any noticeable
build-up of waste material.
- On all bridges, and within 100 feet of bridges, pavement marking waste should be
retained and may be released outside of these areas as long as the discharge does not
cause a noticeable build-up of waste material or where it would likely runoff into a
waterway. For these areas, pavement marking waste may also be collected and disposed
at a permitted landfill.
- In areas with storm sewer drainage from the roadway, the pavement marking waste
material must be collected. This collected waste must be disposed at a permitted landfill
after all water in the waste, if any, has been decanted from the waste. Process water and
decanted water must be disposed at a wastewater treatment facility.
5.36 NCHRP 350 CRASHWORTHY WORK ZONE DEVICES
NCHRP 350 (National Cooperative Highway Research Program 350) Report is the
national standard for crash testing work zone signs and devices. The FHWA, in a
letter to the Department on August 28, 1998 mandates that all work zone signs and
devices being used on the National Highway System be NCHRP 350 compliant. The letter
divided the various types of signs and devices into four categories. The Department
has determined that all work zone signs and devices used on the entire Department
administered highway system be NCHRP 350 compliant. This DOES NOT include county
roads or city streets.
The four categories of work zone devices are defined as follows:
- Category 1 includes those items that are small and lightweight,
channelizing and delineating devices that have been in common use for
many years and are known to be crashworthy by crash testing of similar
devices or years of demonstrable safe performance. These include cones,
tubular markers, flexible delineator posts, and plastic drums with no
attachments.
- Category 2 includes devices that are not expected to produce significant
vehicular velocity change, but may otherwise be hazardous. Examples of
this class are barricades, portable sign supports, intrusion alarms, and
drums, vertical panels, or cones with lights. Testing of devices in this
category will be required. However, they may qualify for the reduced testing
requirements.
- Category 3 is for hardware that is expected to cause significant velocity
changes or other potentially harmful reactions to impacting vehicles. Hardware
in this category must be tested to the full requirement of NCHRP 350. Barriers,
fixed sign supports, crash cushions, and other work zone devices not meeting the
definitions of Category 1 or 2 are examples from this category.
- Category 4 includes portable or trailer-mounted devices such as Arrow
Displays, Temporary Traffic Signals, Area Lighting Supports, and Portable
Changeable Message Signs.
Specification requirements for NCHRP 350 compliant devices are found in
Specification Article 2528.01, sixth
and seventh paragraphs. A list of FHWA approved NCHRP 350 compliant devices can be
found through the Internet at:
http://safety.fhwa.
dot.gov/fourthlevel/hardware/wzd.htm
Contractors have the responsibility to provide documentation to the administering
RCE Office that all work zone signs and devices used on the contract are NCHRP 350
compliant. This documentation should be on contractor letterhead and shall include
the vendor's self-certification for Category I signs and devices and the FHWA "WZ-XX"
acceptance memorandum for Category II signs and devices. A sample documentation letter
is included in Appendix 5-4.
5.37 INSTALLATION OF TRAFFIC CONTROL ZONES
Temporary traffic control devices are always installed in the direction that
traffic flows...that is, "downstream." The first device placed on the roadway is
the first advance warning sign, typically the "ROAD WORK AHEAD" sign. The
installation then proceeds with the signs in the advance warning zone and continues
through the transition zone into the actual work area and finishes in the termination
zone.
All vehicles used to carry the temporary traffic control devices need to be parked
in a safe location such as on the shoulder or at a field entrance, or parked legally at
a marked parking stall or on the curb line in urban areas. These vehicles should display
their four way flashers and any amber flashing or rotating warning lights.
All semi-permanent or permanent traffic control zones should be reviewed prior to
the actual installation time. This review should consist of "pre-marking" the location
of all signs and devices. Pre-marking sign and device locations early should help to
determine if corrections or modifications need to be made to the traffic control plan
included in the contract documents. Any corrections necessary should be according to
Construction Manual Section 5.22.
5.38 SIGNALIZED VS. FLAGGER CONTROLLED HAUL ROAD CROSSINGS
The Office of Design typically determines the need for haul road crossings during
project design. These crossings are decided to be either a signalized or flagger
controlled crossing based on factors such as economic analysis, safety concerns,
and project uniformity. Occasionally necessary haul road crossings are not included
in the plans or field conditions are different from plan details and additional haul
road crossings need to be added.
When haul road crossings are added in the field, RCE offices should review the flow
chart in Appendix 5-7 to determine the appropriate
haul road crossing to use. Questions pertaining to haul road crossings should be referred
to the Office of Construction.
5.39 TRAFFIC CONTROL EVALUATION REPORTING FORM
The Construction Traffic Control Process Improvement Team has developed the
Traffic Control Evaluation Report (Form 830437) to help foster better communication
between the contracting authority and the contractor regarding traffic control
operation and effectiveness. A copy of this form is found in
Appendix 5-10.
The intent of the form is to provide contractors with an easily understood
evaluation during any point of time while a project is under construction. Use
of this form should help modify a contractor’s performance by documenting the
engineer's concern during a project. As stated on the form, the use of this form
and its distribution is solely between the engineer and contractor. Additional
distribution is not needed.
Instructions for completing the form are shown on the backside of the form.
